Ep.3 Data Structures and Algorithms with JS - Lists
Be advised! This post is part of the series: Data Structures and Algorithms with JS therefore before continue to read I suggest you the introduction to this series of posts if you haven't read yet. Thanks.
Let's get start and see how data structures can help us design better software solutions...today I'm going to talk briefly about Lists
Lists
Answer out and loud what are lists? ... Yes that's it. We all intuitively understand what lists are but to be more clear Lists are simply a collection of items therefore a To-Do list, Grocery shop list, book list, Phone number list and so on.
In computer programing Lists are under the ADT (Abstract Data Type) category and can have order/or not (each element has your position) where the element can be duplicated or there's no restrictions on different data types but usually assumed to have the same data type so lists are useful when search and sorted order isn't in need which otherwise would perform a slow and complex data structure design.
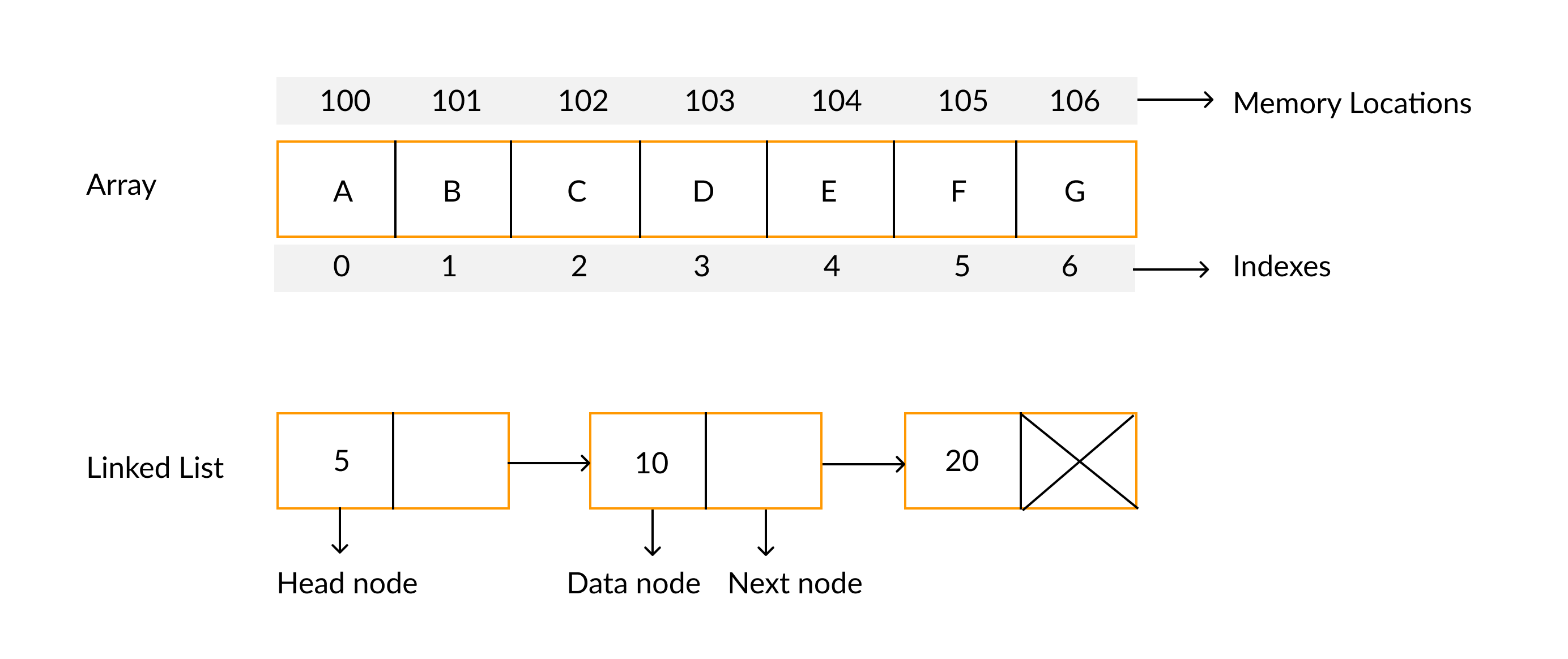
A list is said to be empty when it contains no elements. The number of elements currently stored is called the length of the list. The beginning of the list is called the head, the end of the list is called the tail.
The basic operations we want on a list is to increase and decrease in size adding and removing new elements..We also want to add or remove elements on any position of the list.. access the element value either to just read or change it.. Access the next or prev based on the current element.. we also want to be able to create new lists or clear one.
So here's our actions.
positioncurrent position in the list where any action will take placecurrPosreturn the position of the current elementclearremove all elements of the listinsertAfterinsert an element after target specified in the listinsertBeforeinsert an element before target specified in the listappendan element to the end of the listremovean element from the listlengthnumber of elements in the listfindan element in the list and return the position of the elementcontainsan element in the list return booleanheadset current position to first element in the listtailset current position to last element in the listprevset the current position one step left of the current position, no change if already at beginningnextset the current position one step right of the current position, no change if already at endmoveTomove current position to specified positionto Stringreturn string representation of the listgetElementreturn element of the current position in the list
That being said lets get our hands dirty.
/**
* List constructor
* @class List
*/
function List() {
this.list = [];
this.position = 0;
this.listSize = 0;
}
/**
* Return current position in the list
* @return {[number]} list current position
* @method currPos
*/
List.prototype.currPos = function () {
return this.position;
};
/**
* Insert element after specified target element in the list
* @method insertAfter
*/
List.prototype.insertAfter = function (after, element) {
var target = this.find(after);
if ( target > -1 ) {
this.list.splice(target + 1, 0, element);
++this.listSize;
return true;
}
};
/**
* Insert element before specified target element in the list
* @method insertBefore
*/
List.prototype.insertBefore = function (before, element) {
var target = this.find(before);
if ( target > 0 ) {
this.list.splice(target, 0, element);
++this.listSize;
return true;
}
};
/**
* Remove specified element in the list
* @param element [specified element in the list to be removed]
* @method remove
*/
List.prototype.remove = function (element) {
var target = this.find(element);
if ( target > -1 ) {
this.list.splice(target, 1);
--this.listSize;
return true;
}
};
/**
* Add element at the next available position
* which is equal to the listSize
* also increment the listSize by 1 when
* adding a new element
* @method append
*/
List.prototype.append = function (element) {
this.list[this.listSize++] = element;
};
/**
* Responsible to return the number of
* books in the list
* @return {[number]} [number of books in the list]
* @method
*/
List.prototype.length = function () {
return this.listSize;
};
/**
* Responsible to check if book list is empty
* @return {Boolean}
* @method isEmpty
*/
List.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
if ( this.listSize < 1 ) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
/**
* Clear all elements in the list
* @method clear
*/
List.prototype.clear = function () {
this.list.length = this.position = 0;
};
/**
* Move current position to the front/first in the list
* @method head
*/
List.prototype.head = function () {
this.position = 0;
};
/**
* Move current position to the end in the list
* @method tail
*/
List.prototype.tail = function () {
this.position = this.listSize;
};
/**
* Set current position on step left/back in the list
* if not at the first element
* @method prev
*/
List.prototype.prev = function () {
if ( this.position !== 0 ) {
--this.position;
}
};
/**
* Set current position on step right in the list
* if not at the end/tail element
* @method next
*/
List.prototype.next = function () {
if ( this.position !== (this.listSize - 1) ) {
++this.position;
}
};
/**
* Return string representation of the list
* @return {[string]} list as string
* @method toString
*/
List.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.list.toString();
};
/**
* Find element and return it's position
* @param {[type]} element [element to be search]
* @return {[number]} element position
* @method find
*/
List.prototype.find = function (element) {
for ( var i = 0; i < this.list.length; ++i ) {
if ( this.list[i] == element ) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
};
/**
* Find an element in the list
* and returns true if exist or false if not
* @param element [element to be added in the list]
* @return {[boolean]}
* @method contains
*/
List.prototype.contains = function (element) {
for ( var i = 0; i < this.list.length; ++i ) {
if ( this.list[i] == element ) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
/**
* Move current to specified position
* @param {[number]} position
* @return {[type]} [description]
*/
List.prototype.moveTo = function (position) {
if ( position >= 0 || position <= (this.listSize - 1) ) {
this.position = position;
}
};
/**
* Return current element in list
* @method getElement
*/
List.prototype.getElement = function () {
return this.list[this.position];
}
/**
* This method was created to log/debug the list
* @debug
*/
List.prototype.debug = function (options) {
var options = options || {};
options.list = options.list || false;
options.position = options.position || false;
options.toString = options.toString || false;
options.getElement = options.getElement || false;
options.listSize = options.listSize || false;
options.contains = options.contains || false;
options.isEmpty = options.isEmpty || false;
if ( options.list ) {
console.log('list >>', this.list);
}
if ( options.position ) {
console.log('position >>', this.currPos() );
}
if ( options.toString ) {
console.log('string >>', this.toString() );
}
if ( options.getElement ) {
console.log('Current element >>', this.getElement() );
}
if ( options.listSize ) {
console.log('List size >>', this.listSize );
}
if ( options.contains ) {
console.log('Contains element >>', this.contains(options.contains) );
}
if ( options.isEmpty ) {
console.log('is empty >>', this.isEmpty() );
}
}
the code example above show all methods and properties our list need to have and I also added a method call debug so we can do some simple debug/log.
Let's create a list of movies and at the end lets use our simple test method
/**
* Movie list
*/
var movies = new List();
// add action
movies.append('Matrix');
movies.append('Inception');
movies.append('The Wolf of Wall Street');
movies.append('Batman');
movies.append('G.I Joe');
movies.append('Interstellar');
// move action
movies.tail();
movies.prev();
movies.moveTo(4);
movies.head();
// delete action
movies.remove('G.I Joe');
// add at specified position
movies.insertAfter('Matrix', 'G.I Joe');
movies.insertBefore('G.I Joe', 'The theory of everything');
// Debug list
movies.debug({
list: true,
position: true,
toString: true,
getElement: true,
listSize: true,
contains: 'Batman',
isEmpty: true
});
And this is was the Ep.3 about Data Structures and Algorithms - Lists.
Cheers!